
Remember also that condensation can cause mould problems too. Remembering that relative humidity is defined as the “the amount of water moisture / vapour in the air, expressed as a percentage, relative to what that air is capable of holding at a given temperature“ – so remember that relative humidity will change as temperature changes as warmer air is capable of holding more water vapour.Īlso, humidity will rise as more water is present, such as after a water leak, and explains why unusual condensation could be a sign of a water leak in your home.

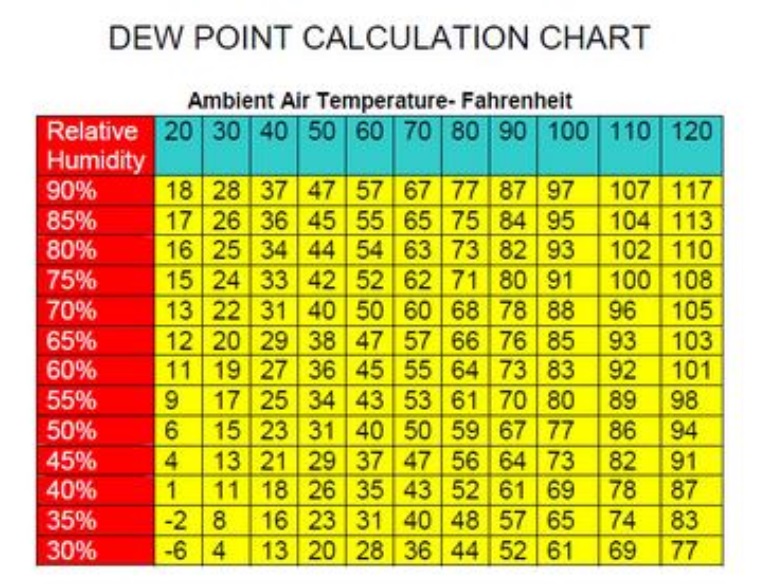
Simply enter the temperature and humidity and we’ll do the rest to give you a useful indication of dew point.īasically water is in the air, in the form of vapour and the amount of this will depend on the relative humidity of the air (the more humid the air, the more moisture it is holding). There is a complicated formula for working out dew point (using temperature and humidity to work it out) but we have made that calculation quick and simple for you with our dew point calculator below. That is a simple example but the same principle applies to other surfaces. It hits the window, which is at or below dew point, and the water condenses hitting a cold spot.

We are all familiar with condensation on windows, especially in bathrooms and laundry rooms in winter – that is a good example because the window will likely be cold and the air in the room, especially after a bath or shower, will be warm and humid. Most commonly it is looked at when looking at bathroom condensation and damp walls etc. Dew Point is simply explained as the temperature at which air is cooled to in order for it to become saturated with moisture and so returns to a state of water droplets (instead of water vapour or steam).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
